Ever caught a glimpse of your reflection and spotted those pesky dark patches that seem to stick around like unwelcome guests? You're certainly not the only one.
It's all too common to see our skin's natural canvas marred by these unsightly marks, leaving us in a loop of frustration as we hunt for solutions.
When it comes to skin discoloration, untangling the mystery between melasma and everyday hyperpigmentation feels like an intricate dance.
Our journey into researching and testing solutions has equipped us with valuable insights aimed at demystifying these complexion conundrums for you.
We’re here to help tease apart melasma from run-of-the-mill hyperpigmentation, examine their distinct triggers, and unearth effective treatments.
So are you ready for some clarity? Let’s embark on this voyage together towards reclaiming that beautifully even glow!
Key Takeaways
- Melasma typically shows up as symmetrical brown or grayish-brown blotches, particularly on the face, while hyperpigmentation is an increase in melanin resulting in dark spots that can vary in shape and size.
- Sun exposure, hormonal changes, aging, and genetics are common contributors to both melasma and hyperpigmentation; sun protection is critical for the prevention and management of these conditions.
- Treatment options for melasma and hyperpigmentation include topical products with ingredients like hydroquinone and retinoids, chemical peels, laser treatments, and prescription medications tailored to individual skin concerns.
- Both melasma and everyday forms of hyperpigmentation can be effectively managed through a combination of professional dermatological treatments and a dedicated home skincare routine.
- It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment plan for skin discoloration to ensure it's suitable for your specific condition.
Difference between Hyperpigmentation and Melasma

Hyperpigmentation is caused by an increase in melanin production, leading to dark patches on the skin, while melasma presents as blotchy, symmetrical brown or greyish-brown patches on the face.
Hyperpigmentation caused by melanin increase
Skin cells produce a pigment called melanin, which gives our skin its color. Sometimes they make too much of it, leading to hyperpigmentation.
This excess melanin can create unwanted dark spots and marks on our skin. These changes in skin color can affect just a small area or may cover larger patches.
Different triggers like sun damage, inflammation from acne scars, or hormonal changes can cause an increase in melanin production.
Freckles and age spots are common examples of hyperpigmentation caused by the sun's UV rays ramping up melanin synthesis as a defense mechanism.
On the other hand, some dark patches come about after an injury to the skin — this is often seen with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation following acne blemishes.
We see these pigmentation disorders show up in varied forms - blotchy patches here, symmetrical patterns there – each telling its own story about underlying causes and potential treatments.
Melasma presents as dark patches symmetrically on the face
Melasma appears as broad, brown, or grayish-brown patches on the skin. These patches are often seen symmetrically on the face, particularly in areas like the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. It is less visible on darker skin tones.
Unlike hyperpigmentation, which is usually very focused and can appear in uneven formations on the skin, melasma presents as more extensive patches with areas of clearing in between.
This distinction helps dermatologists differentiate between melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation when determining appropriate treatment options.
The development of melasma is associated with hormonal changes and sun exposure. It is also common among women who are pregnant or taking hormonal birth control.
Causes of Melasma and Hyperpigmentation

Sun exposure, hormonal factors, aging, and genetics are common causes of both melasma and hyperpigmentation.
Understanding these factors can help in determining the appropriate treatment and prevention methods for each condition.
Sun exposure
Sun exposure contributes significantly to both melasma and hyperpigmentation. The harmful UV rays from the sun stimulate the production of melanin, leading to dark patches on the skin.
Melasma is particularly influenced by sun exposure, with the condition worsening when skin is exposed to sunlight.
Similarly, hyperpigmentation can be exacerbated by prolonged periods of sun exposure, causing existing pigmented areas to darken further and new ones to develop.
Hormonal factors
Hormonal factors play a significant role in the development of both melasma and hyperpigmentation.
For instance, hormonal changes during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills can trigger melasma, often causing dark patches to appear on the face.
Similarly, fluctuations in hormone levels can contribute to the occurrence of hyperpigmentation, leading to areas of skin discoloration due to increased melanin production.
In addition to pregnancy and birth control use, hormonal imbalances during menopause can also influence the appearance of melasma and hyperpigmentation. Moreover, certain medications that affect hormone levels may exacerbate these conditions.
Aging
As we age, our skin undergoes natural changes that can contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation and melasma.
The aging process often leads to a decrease in collagen production, making the skin more susceptible to damage from sun exposure and hormonal fluctuations.
Additionally, as we get older, the effects of cumulative sun exposure become more apparent on the skin, leading to an increased risk of developing dark patches and discoloration.
Other factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and inflammation can also play a significant role in the development of hyperpigmentation and melasma.
As we age, our body's ability to repair itself diminishes; this can prolong the healing process for any damage caused by environmental factors or hormonal changes. These prolonged healing responses may lead to dark spots or patchy areas on the skin that are characteristic of both hyperpigmentation and melasma.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in both melasma and hyperpigmentation. Individuals with a family history of these conditions may have an increased predisposition to developing them.
Research suggests that certain genetic factors can influence the production and distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
Additionally, variations in genes associated with hormonal regulation and inflammation may contribute to the development of melasma and hyperpigmentation.
Understanding the genetic underpinnings of these skin conditions can help tailor treatment approaches and preventive strategies based on an individual's unique genetic makeup.
Both melasma and hyperpigmentation have complex etiologies involving interactions between genetic predispositions and external factors such as sun exposure or hormonal fluctuations.
Treatment Options for Melasma and Hyperpigmentation
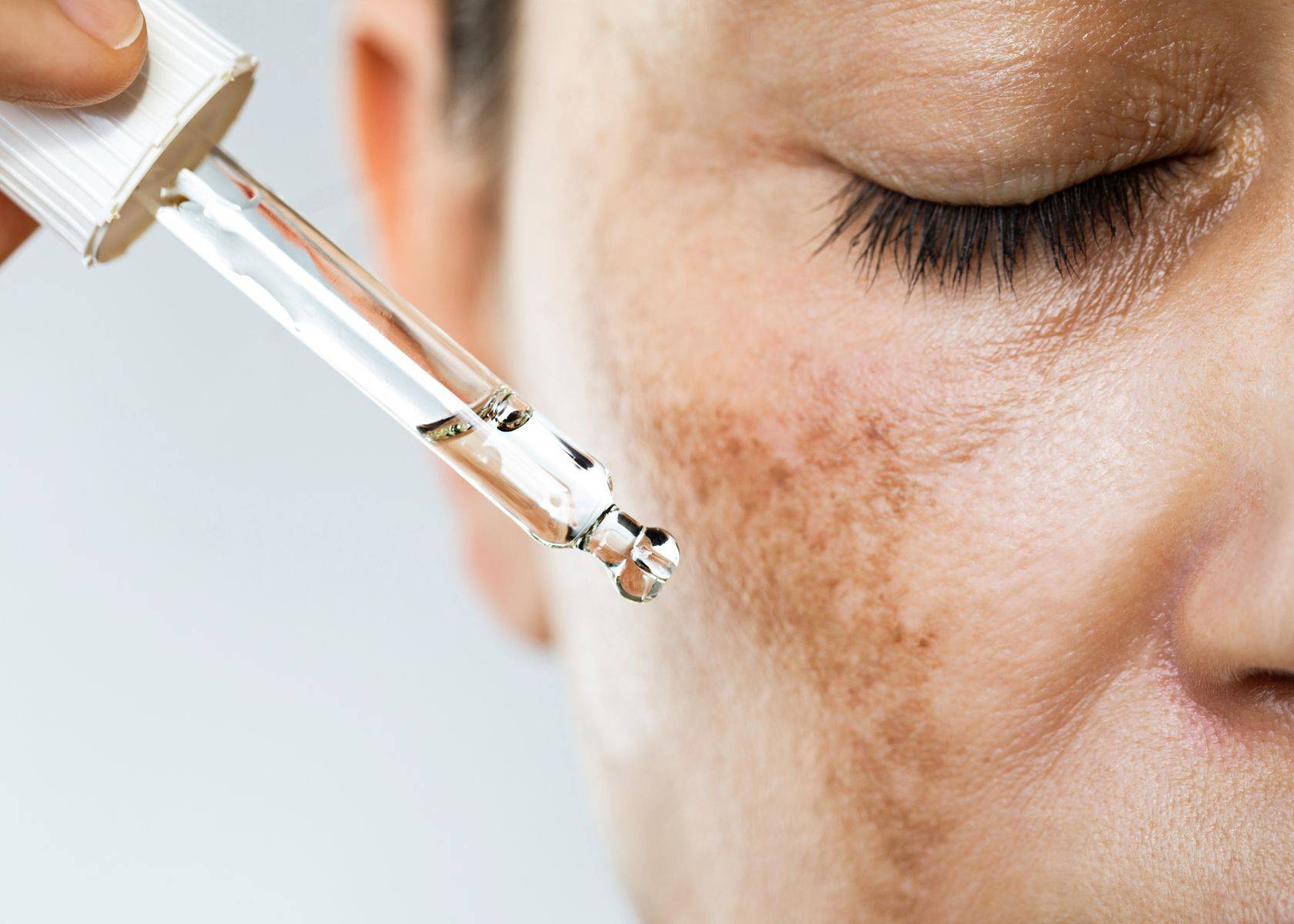
Topical skincare products, chemical peels, laser treatments, and medication-induced treatments are some of the options available to treat hyperpigmentation and melasma. To learn more about these treatment options and how they can help manage these skin conditions, keep reading!
Topical skincare products
Topical treatments play a crucial role in managing both melasma and hyperpigmentation.
These products typically contain ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, niacinamide, and azelaic acid that can help lighten dark patches and even out skin tone.
Hydroquinone is effective in reducing the production of melanin, which contributes to hyperpigmentation.
Vitamin C helps to brighten the skin by inhibiting melanin production and reducing inflammation associated with melasma.
Retinoids promote cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots and encourage new skin growth. Niacinamide has been shown to reduce the transfer of pigment within the skin cells while azelaic acid works as a tyrosine inhibitor - an enzyme involved in melanin synthesis.
When used consistently as part of a comprehensive skincare regimen, these topical products can aid in minimizing the appearance of both melasma and hyperpigmentation.
Chemical peels
Chemical peels are an effective treatment option for both melasma and hyperpigmentation. They work by removing the top layers of skin, where discoloration often resides.
During a chemical peel, a solution is applied to the skin, causing it to blister and eventually peel off. This process stimulates new tissue growth and reveals smoother, more even-toned skin underneath.
Chemical peels can vary in intensity, from superficial to deep, depending on the severity of pigmentation and individual skin type.
Superficial peels are milder and may require multiple treatments for optimal results, while deeper peels can provide more dramatic improvement with just one session but require longer downtime for recovery.
It's important to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional before undergoing a chemical peel to determine which type of peel is best suited for your specific skin concerns and needs.
Laser treatments
Laser treatments offer effective options for addressing both melasma and hyperpigmentation. The procedure involves the use of targeted laser energy to break up excess pigment in the skin, leading to a more even skin tone.
Laser therapy can be particularly beneficial for treating melasma, as it can target deeper layers of pigmentation that topical products may not reach.
Additionally, laser treatments stimulate collagen production, which can help improve overall skin quality and reduce the appearance of dark patches.
It's essential to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most suitable type of laser treatment based on individual skin concerns and conditions.
In some cases, multiple sessions may be required for optimal results with laser treatments. It's crucial to follow post-treatment care instructions diligently, including sun protection measures, to ensure the best outcome from this approach.
Medication-induced treatments
Medication-induced treatments for melasma and hyperpigmentation may be prescribed by dermatologists to address underlying factors contributing to these skin conditions.
Certain medications, such as topical creams containing hydroquinone or tretinoin, may be recommended to regulate melanin production and promote skin cell turnover.
Additionally, oral medications like tranexamic acid or specific combinations of drugs can also be utilized in a targeted approach for managing melasma and hyperpigmentation.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication-based treatment regimen due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Moving forward, it's essential to explore the role of topical skincare products in treating melasma and hyperpigmentation effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions

If you want to treat skin discoloration and acne scarring due to excessive sun exposure, hormonal changes, or any other reasons, here are some of your questions answered.
What is hyperpigmentation and how is it different from melasma?
Hyperpigmentation refers to skin color changes that are not necessarily dead skin cells that turn parts of the skin darker due to various causes, while melasma specifically shows up as symmetrical brown or greyish-brown patches often related to hormonal changes.
Can you see the difference between hyperpigmentation and melasma just by looking at your skin?
Yes, you can often spot the difference: melasma usually appears as symmetrical patches on areas like the cheeks and forehead, whereas hyperpigmentation can show up anywhere and doesn't always have a set pattern.
Are there specific triggers for melasma?
Melasma symptoms are frequently triggered by things like pregnancy or birth control pills which affect hormones, unlike general hyperpigmentation that might result from sun damage or acne scars.
Do dermatological conditions like melasma and others need different treatments?
Yes, treatments may differ since these conditions have unique causes; therefore, it's important to get a proper diagnosis from a skincare expert for targeted treatment plans.
Conclusion
Untangling the intricacies between melasma and hyperpigmentation can feel like a challenging task, but arming yourself with knowledge about their distinguishing traits, triggers, and treatments is the first step to reclaiming clear, even-toned skin.
While these conditions share some similarities, recognizing their unique characteristics is key to selecting targeted solutions.
Don't lose hope – with a strategic skincare routine, professional treatments like chemical peels and laser therapy, and vigilant sun protection, you can dim those dark spots for good.
Share in the comments section below if you have any questions.
Read More About Other Related Topics of Hyperpigmentation





